Teaching production planning and MRP software like drinking water
Production planning is an administrative process to ensure that an adequate supply of raw materials, employees, and other essential factors are prepared and ready for the production of final products according to a specified schedule. This article provides a step-by-step guide to production planning training. If you intend to learn MRP software like drinking water, stay with us.
Teaching Production Planning in 5 Steps
Training in production planning is one of the most crucial stages of production management, essentially serving as the nervous system of a manufacturing organization. In production-oriented entities, it is essential for manufacturing to be carried out with the least cost, in the best possible manner, ensuring high-quality products are produced at the right time.
This can only be guaranteed through effective production planning. However, merely providing training in production planning doesn’t solve the problem, as production plans lack self-execution and do not lead to automatic
implementation.
To achieve this, the production manager must take specific steps. For instance, they need to set job assignments, monitor progress, and devise methods to align actual performance with planned performance.
This involves ensuring that executed plans are adhered to and standards are defined. Therefore, production control becomes a directive function, encompassing the coordination and integration of various production factors’ operations and activities with the goal of optimizing efficiency.
In other words, teaching production planning step by step includes planning, routing, scheduling, distribution, and acceleration.
Planning
The first crucial step in teaching production planning is related to creating accurate production plans. Production plans specify what, where, in what quantity, by whom, and how something should be produced. For precise operational planning, relevant information can be gathered from various sources within the company.
The required information regarding the quantity and quality of produced goods can be obtained from customer orders and sales budgets, while information related to production facilities can be acquired from management and engineering departments.
Therefore, the function of planning formulates production plans and translates them into the requirements of individuals, machinery, and materials.
Regardless of the specific scope of a planning course, production planning contributes to preventing randomness in production, providing a steady and organized flow of production activities, maximizing the utilization of production facilities to minimize operational costs, and aiding in the execution of delivery schedules.
Coordinating different sections of the company to maintain a proper balance of activities and, most importantly, establishing a control framework within the company are among the implementable actions that can be achieved through proper planning.
Routing
The next significant aspect in teaching production planning is routing, which involves determining the path of raw materials through various machines and operations within the factory. Routing encompasses planning the work location, designating the task performer, specifying the path the work should follow, and arranging the necessary sequence of operations.
To determine this path, emphasis is placed on operational data, which usually includes the “where and by whom” of the work, the route it should take, and the required sequence of operations. This operational data is used to create a routing chart, illustrating the sequence of operations and the machines involved.
If a machine breakdown is indicated on the routing chart, alternative routing might also be included. The most efficient routing might be jeopardized if specific machines are unavailable at a given time. In other words, operations routing determines the path, sequence, and appropriate class of machinery and personnel needed for these operations.
From the above, it can be inferred that routing is a vital element and primary consideration in teaching production planning, as many control functions are closely linked and dependent on routing functions.
Therefore, solving various issues regarding suitable personnel, maximizing machine utilization, and accurately determining required time in the production process is essential.
Scheduling
Scheduling involves planning the temporal aspect of production, meaning setting predetermined times for tasks to be performed. This includes determining start and completion times for various operations that need to be carried out. In essence, the scheduling function dictates when an operation must be performed or when a task should be completed.
The nuances of scheduling lie in the details of the timing sequence. For effective work, scheduling, as part of the control function, determines when each called-for operation in the routing sheet must take place in a designated machine to meet the desired delivery dates.
Good control not only directs the initiation time of each specific operation but also indicates the progress of each production piece, the workload on each device, and the availability of each device for new assignments.
Programs are divided into two types: master scheduling and detailed scheduling. Activities, if recorded by the shop, create the master schedule, while detailed schedules are exclusively used for the planning of production and assembly operations required for each product.
Dispatching
Dispatching is a part of the production planning teaching process that converts paperwork into actual production. This function coordinates and translates the planning into actual production. Dispatching is performed in line with the details worked out in routing and scheduling functions.
Hence, dispatching focuses on ensuring materials are transferred to the correct workstations, tools are ready at suitable locations for specific operations, and work moves according to the routing instructions. Essentially, dispatching performs the physical tasks as per the proposed planning.
Thus, dispatching involves issuing or releasing work orders. These work orders indicate production authority and contain the following information:
- Product name
- Sub-assembly or final assembly part to be produced
- Order number
- Quantity to be produced
- Required operation details and their sequence
- Sections involved in each operation
- Tools required for specific operation
- Machines involved in each operation and operation start date
Expediting
Expediting is the final stage in the production planning teaching process. This function is designed to track work efforts. Its purpose is to ensure the execution of what was planned and scheduled.
Expediting involves reporting production data and reviewing variances against pre-established schedules. The main idea behind expediting is to see if the commitment is supported by actual performance. Expediting includes the following functions:
- Ensuring all materials, tools, parts, and accessories are available in specified quantities for starting and completing production operations at all work centers.
- Checking the work-in-process and completed status at various workstations. This involves collecting information about start and completion times, the status of work in progress compared to scheduled completion dates, the movement of materials, parts, and sub-assemblies within the plant, and inspection results.
- Maintaining progress records and updating control boards.
- Reporting to production management about significant deviations to initiate corrective actions. It also involves reporting to the production planning department for future adjustments.
By completing the above stages, teaching production planning ensures the production of quality goods, appropriate quantity, and competitive market rates.
Note:
It should be noted that teaching production planning is an ongoing process, and its various functions are interdependent on each other.
Objectives of MRP Software Training
The ultimate goal of all manufacturing companies is to achieve maximum profit. To attain this goal, the utilization of an essential production process is necessary. Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP) software is a tool used to control and plan for inventory and items. Hence, training in production planning is highly significant for organizations.
Among the objectives of MRP software training are the following:
- Familiarizing users with fundamental concepts of production resource planning, such as understanding the functioning of MRP, key definitions, and basic principles related to this field.
- Learning how to use different sections of the software for production planning, inventory management, and production process control.
- Efficiently managing inventory and scheduling through optimized production planning.
- Developing the ability to allocate resources and plan materials, utilizing the software to incorporate recycled materials into the production chain.
- Managing material supply and balancing inventory and demand to reduce production delays and enhance resource scheduling.
- Enhancing accuracy in production planning and inventory management, reducing errors, and improving the quality of manufactured products.
- Utilizing improved experiences and necessary changes in production and management processes.
- Learning how to align processes with changes in requests and production and management needs.
In MRP software training, what systems are used?
Two systems, namely the general review system and the specific review system, are employed in MRP software training.
General Review System
In this system, at regular intervals such as weekly or monthly, fundamental software plans are reviewed and necessary adjustments are made. In MRP software training, the general review system involves evaluating and refining the content, methods, and instructional approaches.
This system comprehensively analyzes the educational community, instructional processes, and the performance of students or users. The primary aim of the general review system is to enhance the quality of training and productivity related to MRP software.
The most critical part of the MRP software training’s general review system is its focus on improving the quality and effectiveness of the training, aligning with the progress trends and market demands. Typically, the following stages are executed within a general review system in MRP software training:
Needs Analysis: During this stage, training needs and objectives are examined. This involves identifying the skills, knowledge, and abilities that students or users need to gain from the MRP software.
Content Evaluation: Training content includes texts, videos, exercises, and other resources provided to students or users. During this stage, the training content is assessed based on its relevance to MRP software concepts to ensure the required concepts and information are effectively conveyed.
Methods of Instructional Review: Instructional methods are evaluated during this stage. This encompasses selecting and optimizing instructional methods such as videos, interactive materials, in-person classes, and more.
Evaluation of Student or User Performance: Assessing the performance of students or users after studying and training allows for the evaluation of their understanding of MRP concepts. This information can lead to necessary improvements in the training process.
Determination of Review and Update Stages: Based on evaluations and needs, the stages for content, instructional methods, and other training aspects are determined. These stages may be executed at specific time intervals or periodically.
Updating Content and Training: Following the analysis of review results and evaluations, content and training might require updating and optimization. This process continues to ensure that training remains synchronized with market changes and user needs.
Specific Review System
In this system, there is no specific schedule, and changes to the software are made whenever needed, keeping the system up to date.
Note
Due to the numerous complexities involved in production planning, companies often use Excel alongside organizational software to facilitate their operations. Therefore, training in production planning using Excel is also of significant importance. Through Excel-based production planning training, you can easily determine what materials to order and in what quantities for each cycle.
The Role of Inputs in MRP Software Training
To provide training for MRP software, companies need to provide three types of inputs, which play a fundamental role in software training. These inputs are as follows:
- Master Production Schedule (MPS): By employing the primary production scheduling, the quantity of products that need to be produced in each period is determined.
- Bill of Materials (BOM): The list of materials and components shows what constitutes the products.
- Inventory Status: The inventory status indicates the stock of items and components in the warehouse. This information enables necessary procurement planning to be conducted.
The Role of Outputs in MRP Software Training
Following the training in production planning, the most significant outputs of MRP software are the production control and inventory reports. These reports can provide substantial assistance to managers in production planning. Additionally, managers can utilize these reports to identify future needs and execute necessary planning.
Outputs play a crucial role in MRP software training. They illustrate to learners how MRP serves as a tool for improving production planning and resource management. Attaining clear and accurate outputs can strengthen users’ skills and knowledge in utilizing the software. Several roles of outputs in MRP software training are outlined in this section:
- Understanding MRP Functionality: Outputs demonstrate to learners how MRP operates, how inventory, demand, and other information are input, and how the software analyzes information and executes production planning.
- Detecting Demand and Inventory Patterns: Outputs show users how to identify demand and inventory patterns using MRP and input the necessary information into the system.
- Sequencing Production and Scheduling: Outputs guide users in adjusting production sequencing based on demand and creating suitable production schedules.
- Inventory and Order Management: Outputs instruct users on how to manage inventory, process orders, and review inventory determinants.
- Forecasting and Resource Allocation: Through outputs, users understand how to allocate production resources based on demand and perform optimizations.
- Change Management: Outputs teach users how to update and reconfigure MRP when demand or inventory undergoes changes.
What Is the Best Production Planning Software?
One of the most significant challenges in production planning is dealing with the changes that occur in factory production planning training. Given that production planning methods undergo frequent changes, MRP software should be designed to accommodate these changes. Ariyan System Company has successfully addressed this issue by providing integrated and standardized software solutions.
The MRP software from Arian System is one of the best MRP software solutions available. By utilizing this software, you can effectively manage various aspects of production planning. With the solutions provided by Arian System, you can carry out your activities accurately and achieve success.
The Arian System production planning software offers a wide range of features and advanced capabilities that help organizations enhance production efficiency, reduce costs, and make substantial improvements in planning and production control.
Using the Arian System MRP software, users can optimize resource scheduling, work distribution, and equipment allocation based on market needs and demands. The software also provides accurate information about inventory levels and requirements, making it easy for organizations to meet demand and supply products as needed.
Furthermore, the software offers analytical reports and advanced algorithms that allow for evaluating the current production status, predicting future market demand, assessing supply chains, and planning for future production.
Therefore, Arian System serves as a powerful tool for controlling, managing, and improving production processes within organizations. It greatly influences crucial decisions made by managers for the future of the production line.
Some of the key features of the Arian System MRP software include:
- Recording production planning based on equipment and analyses
- Providing daily production schedules
- Specifying production order types based on documents
- Setting limitations on the number of issuances for the production section
- Recording consumption and waste information
- Registering production orders based on inventory and customers
- Logging machine downtime information
- Providing time sheets for product manufacturing based on operation descriptions and product types
- Recording production reports and transmitting information from production to inventory and destination stations
- Generating reports on waste and deviations based on date, operational period, personnel, and customers
To learn more about the Arian System MRP software and to obtain it, you can visit the Production Planning Software page and review its features.
Training for Arian System MRP Software
Production planning is a key factor in the success of organizations. Therefore, practical training in production planning is of high importance. MRP software training helps organizations prevent capital accumulation through production scheduling, reduce waste, and meet customer needs by timely material supply.
After purchasing the Arian System MRP software and its installation by customers, a free training session is provided by installation experts. Necessary training for working with the software is provided, and any questions are addressed.
Following the training session, free customer support is initiated by Arian System. In case customers encounter difficulties while using the software, they can easily receive guidance and necessary assistance through the support team via ticket submission and communication.
It’s worth mentioning that if required, customers can request additional training sessions for working with the software, and a second training session will be arranged.
Conclusion
Production planning helps you meet product demand, optimize process flow, reduce lead times, and efficiently manage your factory, equipment, and inventory. To achieve this, align your production plan with your business strategy and business model and support production planning by coordinating with other departments like procurement, finance, and marketing. To succeed in production planning, an organization needs to employ a Production Planning Software, also known as MRP. If you have any questions or comments about the production planning tutorial, please feel free to reach out to us through the comments section.

 ariansystem
ariansystem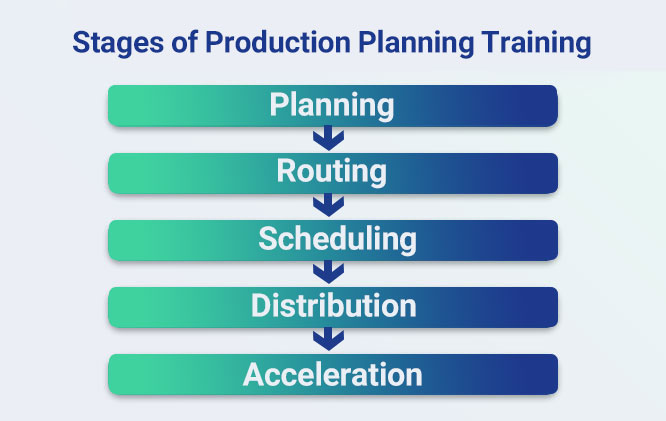



 ariansystem
ariansystem
Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!